Application of laser cutting head in sheet metal industry
Traditional machining methods in sheet metal shops include cutting, blanking and bending. Among them, the blanking process requires a large number of molds, and has the characteristics of less cutting and no cutting. When processing products, dozens of molds are usually equipped, and even some products may require hundreds of molds. From an economic point of view, the cost of a product equipped with a large number of molds increases accordingly, resulting in a waste of money. In order to adapt to modern sheet metal processing, reduce production costs, and improve the level of processing technology, laser head processing technology came into being.

With the application of laser cutting head, sheet metal processing technology has developed rapidly and brought revolutionary ideas to sheet metal processing. Laser cutting head technology and laser cutting head equipment have been familiar and accepted by most sheet metal processing enterprises, and gradually replace traditional sheet metal cutting equipment (mainly CNC equipment, including shearing machine, punching machine, flame cutting, plasma Cutting, high-pressure water) cutting and other traditional sheet metal processing equipment) have the advantages of high processing efficiency, high processing accuracy, good cutting section quality, three-dimensional cutting and so on.

Laser head processing technology plays a very important role in sheet metal processing technology. It improves the labor productivity of sheet metal processing and promotes the development of sheet metal processing. The laser cutting head has high flexibility, which can greatly reduce the processing cycle, cut quickly, produce high efficiency, improve processing accuracy and speed up product development. These advantages have attracted the attention of many manufacturing companies.
The laser cutting head focuses the laser light emitted by the laser head into a laser beam with high power density through an optical path system. A laser beam irradiates the surface of the workpiece to bring the workpiece to its melting or boiling point, and a high-pressure gas coaxial with the beam blows the molten or vaporized metal away. As the relative position between the beam and the workpiece moves, the material eventually forms a slit for the purpose of cutting. Laser cutting heads use invisible beams of light instead of traditional mechanical knives. It has the characteristics of high precision, fast cutting speed, unlimited cutting patterns, automatic typesetting, material saving, smooth incision and low processing cost. It will gradually improve or replace traditional metal cutting equipment.

The mechanical parts of the laser cutting head do not come into contact with the workpiece and do not scratch the surface of the workpiece during operation. Laser cutting is fast, the incision is smooth and flat, and no follow-up treatment is usually required. The cutting heat-affected zone is small, the plate deformation is small, and the joint is narrow (0.10.3 mm); the incision has no mechanical stress and no shear burr. Good repeatability, no damage to the surface of the material, CNC programming, can process any plan, wide cutting the entire board, no need to develop molds, economical and time-saving. Generally, it is recommended to use the laser cutting head for carbon steel plates within 12mm and stainless steel plates within 10mm.
The laser cutting head has no cutting force, no deformation, no tool wear, and good material adaptability. Both simple and complex parts can be shaped and cut accurately and quickly by the laser. It can realize automatic cutting and nesting, improve material utilization, and achieve good economic benefits.
Classification of laser cutting machines: According to different laser generators, there are about three types of laser cutting machines on the market: CO2 laser cutting heads, YAG (solid-state) laser cutting heads and fiber laser cutting heads.
(1) CO2 laser cutting machine: It can stably cut carbon steel within 20mm, stainless steel within 10mm and aluminum alloy within 8mm.
The wavelength of CO2 laser is 10.6μm, which is relatively easily absorbed by non-metals. It can cut high-quality non-metal materials, such as wood, acrylic, PP, plexiglass, etc., but the photoelectric conversion rate of CO2 laser is only about 10%. The CO2 laser cutting machine is equipped with a nozzle for injecting oxygen, compressed air or inert gas N2 at the beam exit to increase the cutting speed and ensure the smoothness and smoothness of the cut. In order to improve the stability and service life of the power supply, the CO2 gas laser must solve the discharge stability of the high-power laser. According to international safety standards, laser hazards are classified into 4 levels, with CO2 lasers being the lowest.
Main advantages: high power, usually between 2000 and 4000 W, can cut various sizes of stainless steel, carbon steel and other conventional materials within 25mm, aluminum plate within 4mm, acrylic plate within 60mm, wood and PVC plate, and Thin sheets can be cut quickly. In addition, since the CO2 laser outputs a continuous laser, the cutting part in the three laser cutting machines is smoother.
Main market positioning: 625 mm plate cutting, mainly for large and medium-sized enterprises and some pure external laser cutting enterprises. Due to insurmountable factors, such as a large number of maintenance losses of lasers and high power consumption of the host, as well as the huge impact of fiber laser cutting machines in recent years, the market is in a state of obvious shrinkage.
(2) The YAG solid-state laser cutting head has the characteristics of low price and good stability, but the energy efficiency is generally lower than 3%.
At present, the output power of products is mostly below 800W W. Due to the low output energy, this product is mainly used for stamping, spot welding and sheet cutting. The green laser beam can be used under pulsed or continuous wave conditions, and has the characteristics of long wavelength and good focusing performance. It is suitable for precision machining, especially hole machining under pulse, cutting, welding, photo-etching and other conditions. The laser wavelength of the YAG solid-state laser cutting head is not easily absorbed by non-metals, so it cannot cut non-metallic materials. The YAG solid-state laser cutting head needs to improve the stability and service life of the power supply. It is necessary to develop large-capacity, long-life optical pump excitation light sources. By using semiconductor optical pumps, energy efficiency can be greatly improved.
Main advantage: It can cut aluminum plate, copper plate and most non-ferrous metal materials, which other laser cutting heads cannot cut. The machine is inexpensive, low usage and easy to maintain. Most of the key technologies have been mastered by domestic enterprises. The price of accessories and maintenance costs are low, and the operation and maintenance of the machine are simple. The quality of employees is not high.
Main market positioning: cutting below 8 mm. It is mainly aimed at SMEs for self-use and sheet metal manufacturing, household appliances manufacturing, kitchenware manufacturing, decoration, advertising and most users in other industries where processing requirements are not particularly high. In the future, it may gradually replace traditional processing equipment such as wire cutting, CNC punching, water jetting and low-power plasma.

(3) The fiber laser cutting head can be transmitted through the optical fiber, which has the characteristics of unprecedented flexibility, less failure points, convenient maintenance and fast speed.
It has great advantages when cutting thin plates within 4mm, but its quality is very poor due to the influence of the solid-state laser wavelength when cutting thick plates. The wavelength of the fiber laser cutting head is 1.06 μm, which is not easily absorbed by non-metals, so it cannot cut non-metallic materials. The photoelectric conversion rate of fiber lasers is as high as 25% or more. In terms of power consumption and supported cooling system parameters, fiber lasers have obvious advantages.
According to international safety standards, fiber lasers are the most harmful type because of their long wavelengths and high eye damage. For safety reasons, fiber laser processing must be performed in a completely enclosed environment. As a new laser head technology, fiber cutting head is far less popular than carbon dioxide laser cutting head.
Main advantages: high photoelectric conversion rate and low power consumption. It can cut stainless steel plates and carbon steel plates within 12mm, and is the fastest laser cutting head for thin plates among the three machines. The gap is fine, the spot quality is good, and it can be used for fine cutting.
Main market positioning: cutting below 12mm, especially for high-precision processing of thin plates. It is mainly aimed at manufacturers who require extremely high machining accuracy and efficiency. It is estimated that with the advent of 5000W and above lasers, fiber laser cutting heads will eventually replace CO2 high power laser cutting heads in most markets.

Laser fusion cutting head
(1) In laser melting and cutting, after the workpiece is partially melted, the melted material is ejected through the airflow. Since the material transfer takes place only in the liquid state, this process is called laser melt cutting.
(2) The laser beam is coupled with the high-purity inert cutting gas to promote the molten material to leave the gap, and the gas itself does not participate in the cutting.
(3) Laser melting cutting can achieve higher cutting speed than gasification cutting. The energy required for gasification is usually higher than the energy required to melt the material. In laser melting cutting, the laser beam is only partially absorbed.
(4) The maximum cutting speed increases with the increase of laser power, but decreases inversely with the increase of plate thickness and material melting temperature. When the laser power is constant, the limiting factors are the gas pressure at the gap and the thermal conductivity of the material.
(5) Non-oxidative cutting of iron and titanium metals can be obtained by laser fusion cutting. For steel, a laser power density that melts but does not evaporate will be produced, and the laser power density is between 104 W/cm2 and 105 W/cm2.
Laser flame cutting head
Laser flame cutting differs from laser melt cutting because it uses oxygen as the cutting gas. Through the interaction between the oxygen and the heated metal, a chemical reaction occurs to further heat the material. For the same thickness of structural steel, the cutting speed obtained by this method is higher than that obtained by fusion cutting.
On the other hand, this method is inferior to fusion cutting in terms of cut quality. In effect, wider slits, pronounced roughness, increased heat-affected area and poor edge quality are produced. Laser flame cutting is flawed (risk of burning sharp corners) when machining precision models and sharp corners. Pulsed mode lasers can be used to confine the heat affected zone. The laser power used determines the cutting speed. At a certain laser power, the limiting factors are the oxygen supply and the thermal conductivity of the material.
Laser gasification cutting head
During laser gasification cutting, the material is gasified at the cutting seam, which requires very high laser power. In order to prevent the material vapor from condensing on the slit walls, the thickness of the material must not greatly exceed the diameter of the laser beam, so this treatment is only suitable for cases where molten material is not discharged. This process is really only used in very small fields of application for iron-based alloys.
This process is not suitable for wood and some ceramics, which typically require thicker cuts.
(1) In laser gasification cutting, the optimal beam focusing depends on the material thickness and beam quality.
(2) The laser power and vaporization heat have a certain influence on the optimal focus position.
(3) When the plate thickness is constant, the maximum cutting speed is inversely proportional to the gasification temperature of the material.
(4) The required laser power density is greater than 108W/cm2, depending on the material, cutting depth and beam focus position.
(5) Under certain plate thickness conditions. Assuming sufficient laser power, the maximum cutting speed is limited by the gas injection rate.
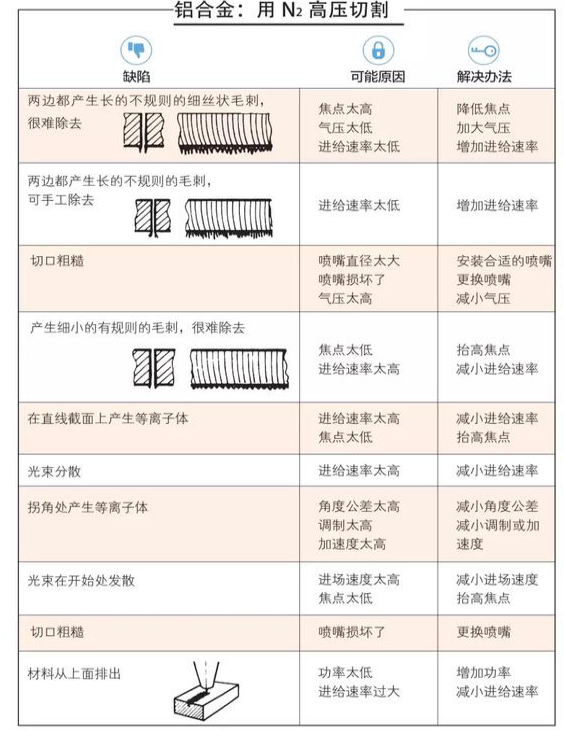
Laser head processing
Machining refers to the interaction between the laser beam, the process gas and the workpiece. Figure 2 shows the processing parameters, cutting process Before cutting, the laser must heat the workpiece to the temperature required to melt and vaporize the material.
The cutting plane consists of an almost vertical plane that absorbs the laser radiation for heating and melting. In laser flame cutting, the flow of oxygen into the slit further heats the melting zone to near boiling temperatures, and the resulting gasification removes the material. At the same time, the liquefied material is discharged from the lower part of the workpiece by the heated gas.
In laser melt cutting, the liquefied material is expelled with the gas, thus protecting the gap from oxidation. The continuous melting zone is gradually slid along the cutting direction to obtain a continuous slit. In this area, many important activities take place during the laser cutting process. Analyzing these activities can obtain important information about laser cutting, calculate cutting speed and explain the formation of pull line characteristics.
Material properties
The result of cutting on the workpiece may be a neat cut, or conversely, there may be rough edges or excessive burn. The most important factor affecting the cutting quality is.
(1) Alloy composition.
Alloy composition affects the strength, specific gravity, weldability, oxidation resistance and acidity of the material to some extent. Some of the important elements in ferroalloy materials include carbon, chromium, nickel, magnesium and zinc.
The higher the carbon content, the more difficult it is to cut the material (the critical value is 0.8% carbon). The following carbon steels have good laser cutting results: St 37-2, StW 22, DIN 1.203.
(2) The basic microstructure of the material.
In general, the finer the particles that make up the material, the better the quality of the cutting edge.
(3) Surface quality and roughness.
If there are rusted areas or oxide layers on the surface, the cut profile will be irregular and many damage points will appear. To cut corrugated board, select the maximum thickness cutting parameter.
(4) Surface treatment.
The most common finishes are galvanized, sprayed, anodized or laminated plastic film coatings. The edges of galvanized sheet are prone to slag formation. For painted panels, cut quality depends on the composition of the coated product.
Plates with layered material coatings are ideal for laser cutting. For trouble-free operation of capacitive inspection and optimum adhesion of the coating (avoiding floating air bubbles), the edge of the coating must always be on the upper part of the workpiece being cut.
(5) Beam reflection.
How the beam is reflected on the workpiece surface depends on the base material, surface roughness and processing method. Certain aluminum alloys, copper, brass and stainless steel plates have high reflectivity. When cutting these materials, special attention should be paid to adjusting the focus position.