The image you uploaded contains information about the "TL552-CD" high-power molten pool temperature-controlled laser processing head.

Product Overview:
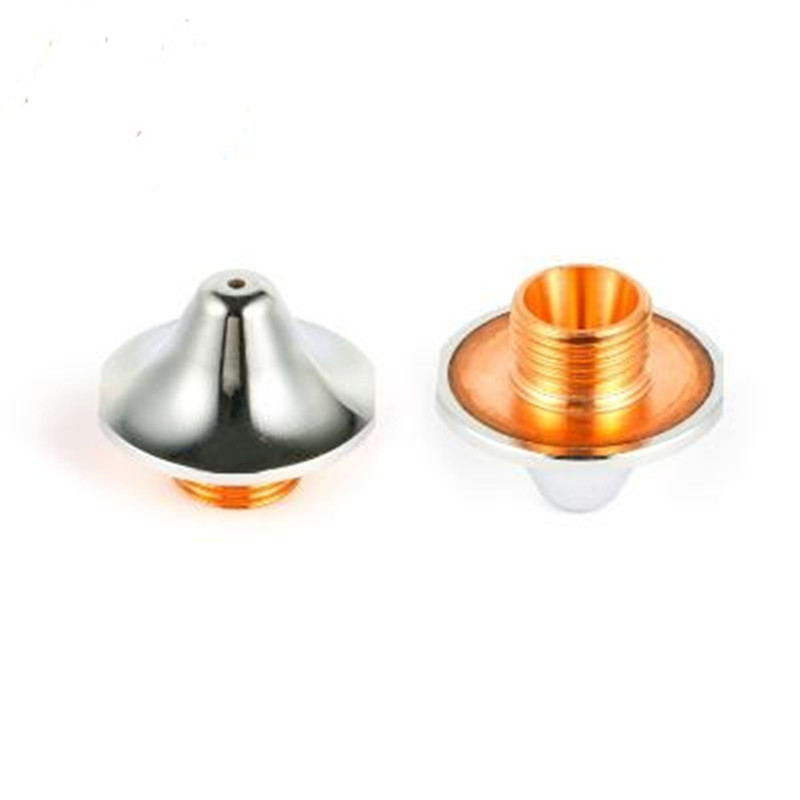
The TL552-CD is designed for high-power laser processing applications and can be used for different material processing scenarios. It features real-time molten pool temperature monitoring, ensuring precise temperature control for better process stability. The head is equipped with high-performance optical systems and a modular structure, allowing flexible integration into various systems. It is especially suitable for demanding industrial processing tasks.
Characteristics:
Modular structure for easy customization and integration.
Internal temperature monitoring for real-time process adjustments.
Adaptable to various optical systems (e.g., QBH).
Compact and lightweight design for easy machine integration.
High precision in maintaining molten pool temperature to enhance stability and consistency.
Technical Parameters:
Power Capacity: 20 kW
Collimation Lens Options: 100 mm or 150 mm
Laser Aperture: φ1-4 mm adaptive fiber laser interface
Focusing Lens Options: 200 mm, 250 mm, 300 mm, 400 mm
Spot Size: φ0.5 mm to 5 mm
Weight: ~6.5 kg (depending on configuration)
This equipment appears to be well-suited for precise and high-power laser cutting or welding tasks, offering temperature control for improved process reliability.
Laser Cladding is a process that utilizes a high-energy-density laser beam to melt and bond coating material with the surface of a substrate. It is widely used in the fields of surface repair, reinforcement, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance. The basic principle involves using a laser beam to rapidly melt the coating material pre-placed on the surface of the workpiece while simultaneously creating a thin layer of molten material on the substrate. As the coating and substrate cool rapidly, they form a metallurgical bond. This cladding layer offers superior physical and chemical properties, significantly improving the surface quality and service life of the workpiece.
Key Features of Laser Cladding:
High Precision: Laser cladding allows precise control over the thickness, shape, and location of the coating, making it suitable for fine processing.
Material Versatility: It can use various materials such as metals, ceramics, and alloys for cladding, adapting to different operational environments.
Metallurgical Bonding: The cladding material forms a metallurgical bond with the substrate, offering high bonding strength and excellent mechanical properties.
Minimal Heat Effect: Due to the high energy density and short interaction time of the laser, the heat-affected zone in laser cladding is small, minimizing material distortion and thermal stress.
High Efficiency: Laser cladding can complete large surface area coatings in a short time, and the process is highly efficient and suitable for automation.
Applications of Laser Cladding:
Surface Repair: Repair of worn, corroded, or broken parts to restore their original dimensions and performance, such as engine parts, pump shafts, and gears.
Surface Reinforcement: Cladding hard materials on the surface to enhance the wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and fatigue resistance of the workpiece, such as tools, molds, and mechanical parts.
Functional Coatings: Applying functional materials on the surface of the substrate to achieve specific surface properties like conductivity, thermal conductivity, or high-temperature resistance.
Equipment Requirements for Laser Cladding:
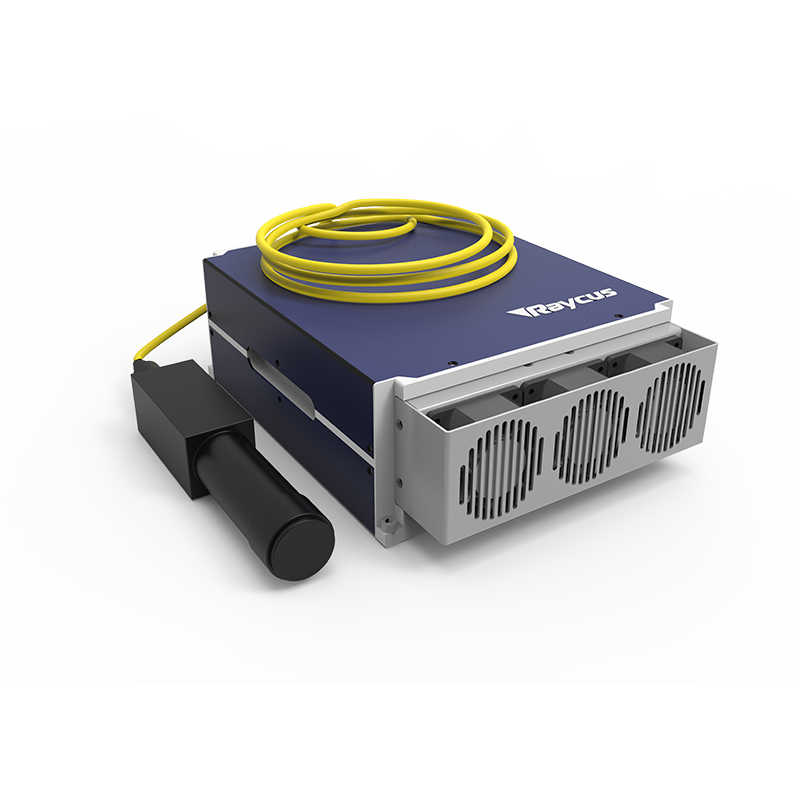
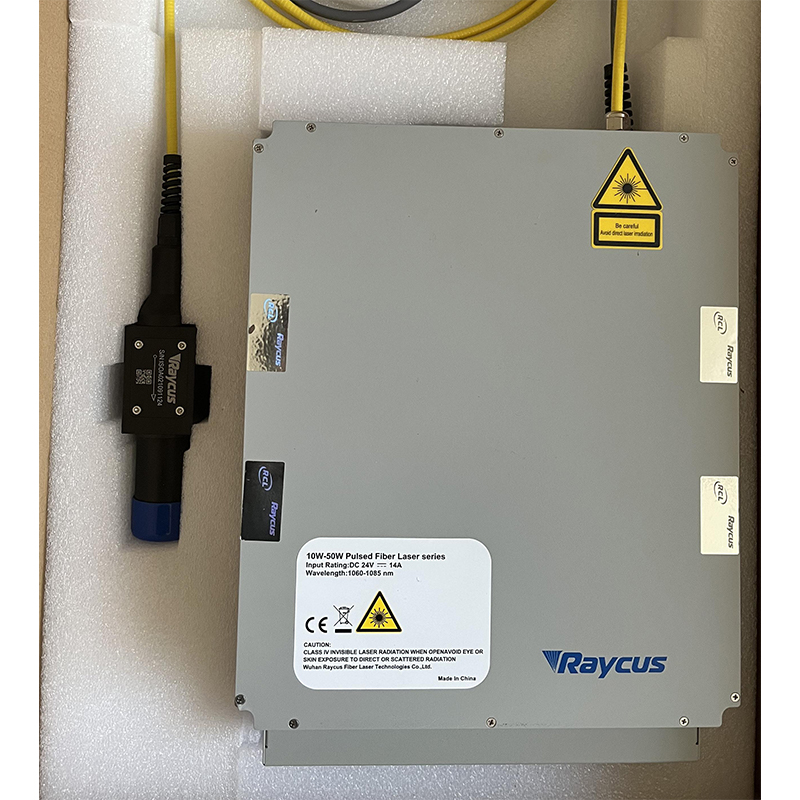
High-power lasers (such as fiber lasers or CO2 lasers).
High-precision cladding heads (like the TL552-CD you mentioned), which offer real-time molten pool temperature monitoring to ensure stable cladding quality.
Suitable powder or wire feeding systems to deliver the coating material to the cladding area.